The North American bulk power system (BPS) is currently undergoing substantial changes in design, control, planning, and operation due to the rapid interconnection of Inverter-Based Resources (IBRs). While inverter technology can provide significant benefits to the BPS, reliability of the grid is at risk if IBRs are not integrated properly. For example, one of the main challenges associated with IBRs is the capability of these resources to “ride through” a disturbance. Generator ride through capability is an essential component of reliable operation of the BPS and performance data has shown that some IBRs halt or limit production of energy during and after a system disturbance.
To address reliability risks associated with IBRs, NERC and the Regional Entities (collectively the ERO Enterprise) developed an Inverter-Based Resource Strategy, which identifies and addresses challenges associated with IBRs and provides risk mitigation techniques and best practices to IBR owners and operators through outreach and education. Part of the IBR strategy is to address a 16% gap in IBR owners and operators that are connected to the bulk power system but fall under the current threshold of NERC registration and are therefore not subject to compliance with mandatory reliability standards. Additionally, the absence of these resources in studies and modeling has contributed to systemic modeling errors and gaps in modeling data, presenting undue risk to reliable operation of the BPS.
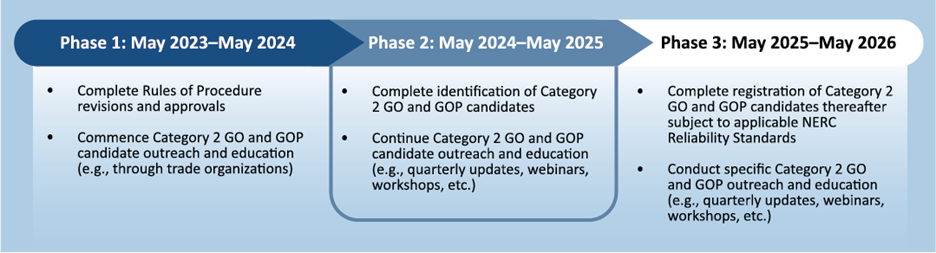
In response to this risk, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) issued an order in May 2023 approving a three-phase work plan filed by NERC to identify and register owners and operators of currently unregistered bulk power system-connected IBRs.
FERC approved revisions to the NERC Rules of Procedure on June 27, 2024, adding the following category of Generator Owners/Generator Operators (GO/GOP) to Appendix 5B Statement of Compliance Registry Criteria.
The ERO Enterprise is providing quarterly updates to industry on the status of key IBR registration activities and milestones achieved. This outreach, along with approved revisions to the NERC Rules of Procedure, concludes Phase 1 of the work plan.
“Category 2” GO/GOP is defined as an entity that owns, maintains, and/or operates non-BES inverter based generating resources that either have or contribute to an aggregate nameplate capacity of greater than or equal to 20 MVA, connected through a system designed primarily for delivering such capacity to a common point of connection at a voltage greater than or equal to 60 kV.
Phase 2—scheduled through May 2025—is currently underway and includes identification of Category 2 GO/GOP candidates, as well as continued outreach and education to industry. NERC sent a request for information (RFI) to Transmission Owners (TOs) and Balancing Authorities (BAs) on July 9, 2024, as part of this effort. The information gathered through the RFI will be used to identify and connect with IBR registration candidates to inform them of the registration obligation, provide education on the reliability standards and requirements, and introduce NERC, the applicable Regional Entity, and the E-ISAC. Responses to the RFI are due to the Regional Entities by September 20,2024, and efforts to register new and existing Category 2 IBRs will take place through May 2026.
Addressing IBR reliability concerns early helps to support the integration of new and existing IBR resources into the BPS and ensures that the energy transformation leads to a more reliable, resilient, and secure power grid.
Questions related to this initiative should be directed to [email protected].
– Pete Pelowski, MRO Senior Reliability Specialist