
Inadequate Inverter Based Resources and Distributed Energy Resources Performance and Modeling
Risk Overview
Inverter-based resources, like solar and wind power, are becoming a larger part of the grid, and consumers are increasingly dependent on these resources for reliable energy. Unlike traditional power plants such as coal and natural gas, which respond based on physics to grid conditions, inverter-based resources rely on software defined behavior. Inadequate coordination of engineering designs of power plants using inverter-based resources has led to unexpected outages during grid disturbances. Additionally, the potential risks of inverter-based resources have not been adequately considered in future grid planning. These factors have caused significant risk to the reliability of the bulk power system. To address these challenges, utilities must take proactive steps in two general areas. One involves utilities closely monitoring grid disturbances and working with inverter-based resource owners and operators to understand, predict, and alter the software defined behavior to a state most advantageous for grid operations. The second is for grid planners to consider the factors that make inverter-based resources different compared to traditional power plants when planning for the future. By doing so, we can better manage the performance of these resources and maintain a stable and reliable power grid.
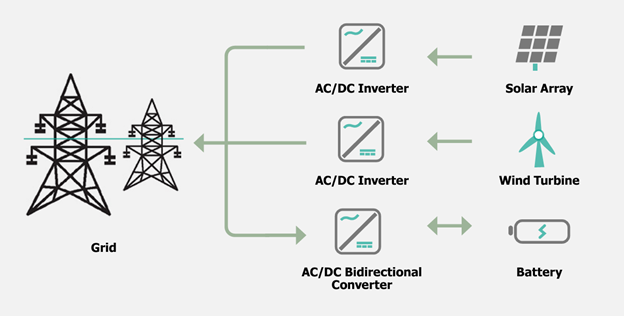
What is an Inverter Based Resource?
Power plants that are typically wind, solar, or batteries connect to the transmission grid with electronics (the inverter) that converts power to a grid compatible form. In smaller house or neighborhood scale powerplants like community solar or a Tesla battery in a garage, the generation is referred to as Distributed Energy Resources. Introduction to Inverter-Based Resources on the Bulk Power System provides more information in an easy to read format.
Key Drivers and Trends
- As fuel-based generation is phased out, inverter based resources are increasingly used to meet energy needs.
- Inverter based resources react quickly to system conditions, which makes it hard to coordinate with the relatively slower response of fuel-driven power plants, and other nearby inverter based resources.
- While inverter based resources individually produce less electricity than fuel-based generation, their combined effect can impact grid reliability.
- Inverter based resources are new to grid-scale use, and engineers are still learning how to accurately apply the technology to achieve the desired electrical performance.
- The vendors of the inverter based resources often lack familiarity with grid operations, thus designing equipment that is not predictable during some operating conditions.
- 95% of the new generation scheduled to be built in the MRO geographic region is inverter based.
Actions to Reduce Risk
- Study how inverters react to real grid disturbances, true-up engineering models to reflect reality, and share findings and corrective actions broadly.
- Follow industry recommendations from the Level 2 NERC Alerts (NERC Alert IBR Model Quality Deficiencies, NERC Alert IBR Performance) to develop and use models for inverter based resources in wide-area studies and interconnection specific analyses, and to ensure that inverter protection settings maximize the availability of the generating resource following a grid disturbance.
- Review the reliability guidelines, white papers, and webinars produced by the Inverter-Based Resource Performance Subcommittee (IRPS). The technical materials are intended to help transmission and generation entities understand the performance aspects, modeling, and system studies of bulk power system connected inverter-based resources.
- Follow the activities under FERC Order 901 directed NERC to modify or create new reliability standards that address inverter based resource deficiencies to understand core issues with inverter based resource performance and modeling.
- Project 2020-02 Modifications to PRC-024 changed the standard to performance-based to ensure that generators remain connected to the grid during disturbances.
- Project 2021-04 Modifications to PRC-002 was initiated to ensure there is adequate data to analyze grid disturbances. This project specifically addresses disturbance monitoring and reporting requirements specific to inverter based resources.
- Project 2023-02 Analysis and Mitigation of BES Inverter Based Resource Performance Issues standard requirements to identify, analyze, and mitigate unexpected inverter based resources change in power output.
- Project 2020-06 Verification of Models and Data for Generators addresses the lack of individual generator unit dynamic models that transmission planners require to study the grid. The project will close the gap between what generator owners provide and what transmission planners need.
- Project 2021-01 System Model Validation with Inverter Based Resources addresses grid models to ensure they match real-world behavior during disturbances and aligning steady state and dynamic models. The project will develop criteria to validate models, and a process to communicate grid model defects discovered to the affected parties.
- Project 2022-02 Uniform Modeling Framework for Inverter Based Resources will develop requirements to standardize modeling so engineering data can be shared amongst all affected parties. The framework will include minimum modeling criteria, data exchange requirements, and considering the performance of Distributed Energy Resources and how they affect grid planning.
Inverter Based Resources Registration Initiative
FERC issued an Order in 2022 directing NERC to identify and register owners and operators of currently unregistered bulk power system-connected inverter based resources. Working closely with industry and stakeholders, NERC is executing a FERC-approved work plan to achieve the identification and registration directive by 2026. NERC and the Regional Entities will work to identify and register new and existing inverter based resources before the deadline of May 2026 listed in the FERC Order. The following links which are available on NERC’s Organization Registration and Certification page provide more information on the initiative.
- Ensuring Grid Reliability Video explains the complexities surrounding inverter based resources and illuminates their role on the grid in concert with traditional generating resources. It also provides a concise overview of the IBR Registration Initiative, detailing objectives and benefits and explaining how registrants can engage with their Regional Entities and NERC through the registration process.
- Inverter-Based Resource Registration Webinar and Slides focused on NERC’s effort to identify and register owners and operators of non-bulk electric system inverter based resources with an aggregate nameplate capacity of ≥20 MVA connected at a voltage ≥60 kV. The webinar featured presentations from NERC, the Electricity Information Sharing Analysis Center (E‑ISAC), and Regional Entity staff on various topics and activities underway.
- IBR Quick Reference Guide provides an overview of the registration milestone, key activities, and key resources.
- IBR Registration FAQ answers questions about proposed revisions to NERC Rules of Procedure to address registration of owners and operators of unregistered inverter based resources.
- Open Letter to New Registrants provides an introduction to NERC, the E-ISAC, and the ERO Enterprise. Additionally, it provides links to key ERO resources.
- Candidate for Registration: A Quick Reference Guide discusses registration with NERC, candidate registration milestones, provides links for information on inverter based resources, and gives a background on NERC and E-ISAC.
Q4 2024 Registration Initiative Update highlights activity from Q4 2024 that was focused on continued outreach to registration candidates and creating resources to aid their entry into the ERO Enterprise.
Charting a Path Towards Improving Inverter Based Resources Performance Issues
There have been 13 bulk power system disturbances since 2016 analyzed by NERC that involved performance issues with inverter based resources. Notably:
- Each event was characterized by significant loss of real power output following a system electrical fault.
- Each of these disturbances involved multiple solar and/or wind resources, which use inverters to generate into the grid.
- Some of these events also included the loss of real power from DER, which simultaneously increases load requirements of the grid.
The disturbance reports, alerts, guidelines, and other deliverables developed by the ERO thus far have highlighted that abnormal inverter based resource performance issues pose a significant risk to bulk power system reliability. Each event analyzed has identified new performance issues, such as momentary cessation, unwarranted inverter or plant-level tripping issues, controller interactions and instabilities, and other critical performance risks that must be mitigated. The most notable events were: Blue Cut Fire (1200 MW Fault Induced Solar Photovoltaic Resource Interruption Disturbance Report), Canyon 2 Fire (900 MW Fault Induced Solar Photovoltaic Resource Interruption Disturbance Report), and Angeles Forest and Palmdale Roost (April and May 2018 Fault Induced Solar Photovoltaic Resource Interruption Disturbance Report). Out of these notable events, NERC issued Level 2 Alerts Industry Recommendation: Loss of Solar Resources during Transmission Disturbances due to Inverter Settings and Industry Recommendation Inverter-Based Resource Model Quality Deficiencies. The alerts provide high level recommendations to improve inverter based resource performance.
In June 2022, NERC published its Inverter-Based Resource Strategy that charts a path towards improving inverter based resources performance issues, which includes supporting improvements to interconnection procedures and requirements, improving modeling, clarifying performance requirements, and increasing event analysis for abnormal performance. These efforts are in progress. There are also several NERC standard projects in development to address some elements of the strategy, and to take action on October 2023 FERC Order 901 which directs NERC to address reliability gaps pertaining to inverter based resources in four areas: data sharing, model validation, planning and operational studies, and performance requirements. See Actions to Reduce Risk on this page for ongoing standards drafting projects that are executing on the order.
In November 2023, FERC Order 2023 in part requires inverter based resource developers to provide models required for transmission providers to do accurate interconnection studies and to configure inverter controls to ride-through system disturbances.
MRO partnered with MISO and Southwest Power Pool (SPP) in 2023 to analyze system disturbances within those entities’ respective footprints for any signs of inverter based resource performance issues. The results showed few issues isolated to individual windfarms and no widespread issues like those seen in the California and Texas events. MRO’s Reliability Advisory Council also published an article in June 2023 on the adoption of the IEEE 1547-2018 standard for Distributed Energy Resources. This article highlighted a reliability guideline developed by NERC’s System Planning Impacts from DER Working Group (SPIDERWG) on the same topic. The article listed key perspectives focused on the ride through capability of DERs and the need to coordinate settings and controls with expected grid operations to maintain reliability.
The NERC System Planning Impacts from DER Working Group (SPIDERWG) has been analyzing the aggregate impacts that distributed energy resources can have on reliable operation of the bulk power system, and develops whitepapers, reliability guidelines, or standard authorization requests to address those impacts. Focus areas of the SPIDERWG are: displacement of generation providing various essential reliability services; balancing generation and demand and ramping requirements; adequate levels of voltage regulation and reactive power support; distributed energy resource ride-through and trip settings; modelling and forecasting of distributed energy resources; and lack of observability or dispatchability of distributed energy resources.
The NERC Inverter-Based Resource Performance Subcommittee (IRPS) is exploring the performance characteristics of utility-scale inverter based resources, and is building off of the experience of the Blue Cut Fire and other fault induced solar generation events. The subcommittee is addressing recommendations from the Blue Cut Fire report including: system analysis, modeling, and reviewing inverter behavior under abnormal system conditions. They are producing technical materials intended to support the utility industry, generation owners with inverter based resources, and equipment manufacturers. Their goal is to clearly articulate recommended inverter based resource performance characteristics, to ensure reliability through system studies, and ensure dynamic modeling capabilities that support grid reliability. Webinars one through seven on the subcommittee homepage provide an easily understandable overview of the technical issues with current inverter based resource power plants, equipment design, and system planning.